Introduction:
In the grand tapestry of the digital era, the Internet of Things (IoT) emerges as a transformative force, weaving an intricate network that connects devices, systems, and people in ways unimaginable just a few decades ago. This article delves into the realm of IoT, exploring its significance, applications, challenges, technological advancements, societal impact, future horizons, and the profound connection it fosters in our interconnected world.
I. Unraveling the IoT Tapestry:
Definition of IoT:
The Internet of Things refers to the interconnected network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and even buildings embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data.
The Web of Connectivity:
At its core, IoT is about creating a web of connectivity that extends beyond traditional computing devices to include everyday objects, creating an intelligent, responsive, and data-driven environment.
II. The Pillars of IoT:

Sensors and Connectivity:
IoT relies heavily on sensors that gather data from the physical world, coupled with robust connectivity solutions that facilitate seamless communication between devices.
Data Processing and Analytics:
The data collected by IoT devices undergoes sophisticated processing and analysis, often leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to derive meaningful insights.
III. Applications Across Industries:

Smart Homes:
In the realm of smart homes, IoT manifests in connected devices like thermostats, security cameras, and voice-activated assistants, creating homes that adapt to the preferences and needs of residents.
Healthcare Revolution:
In healthcare, IoT devices such as wearables and monitoring systems enable real-time health tracking, fostering preventive care and personalized treatment plans.
Industrial IoT (IIoT):
Industries embrace IoT for predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and overall operational efficiency, ushering in the era of Industry 4.0.
Smart Cities:
IoT plays a pivotal role in building smart cities, where connected infrastructure, intelligent traffic management, and efficient public services enhance the quality of urban life.
IV. The Impact on Daily Life:

Enhanced Convenience:
From smart refrigerators that automatically restock groceries to wearable devices that track fitness metrics, IoT enhances daily life by providing unprecedented levels of convenience.
Environmental Sustainability:
IoT contributes to environmental sustainability through smart energy grids, waste management systems, and efficient resource utilization, reducing the ecological footprint.
V. Challenges and Considerations:

Security Concerns:
The interconnected nature of IoT raises security challenges, requiring robust measures to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Interoperability:
Ensuring that diverse IoT devices can communicate seamlessly remains a challenge, necessitating standardized protocols for interoperability.
Privacy Considerations:
The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices raises concerns about individual privacy, prompting discussions on how to balance technological innovation with privacy rights.
VI. Societal Impact:

Empowering Smart Communities:
IoT has the potential to empower entire communities, fostering interconnectedness and collaboration for improved living standards, resource management, and overall well-being.
VII. The Role of 5G in Advancing IoT:
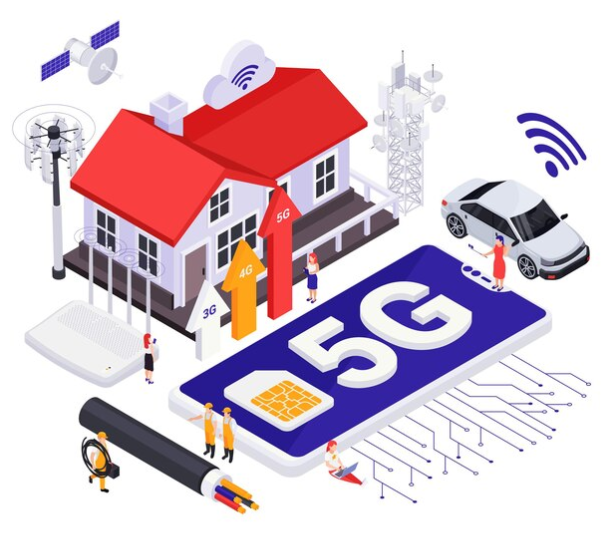

Next-Generation Connectivity:
The rollout of 5G networks represents a significant leap forward for IoT, providing faster and more reliable connectivity. This facilitates the real-time communication essential for applications like autonomous vehicles and smart infrastructure.
Edge Computing’s Integration:
As 5G proliferates, the integration of edge computing becomes more pronounced, allowing data processing to occur closer to the source. This not only reduces latency but also enhances the responsiveness of IoT systems, crucial for applications requiring near-instantaneous decision-making.
VIII. Future Horizons:

Artificial Intelligence at the Core:
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into IoT systems is set to redefine how devices interact and interpret data. AI will enable devices to become more intelligent and adaptive, learning from user behavior to enhance functionality.
Blockchain for Enhanced Security:
The utilization of blockchain technology is emerging as a solution to address security concerns. By providing a decentralized and tamper-resistant way of recording transactions, blockchain enhances the security and integrity of data in IoT networks.
IoT in Agriculture:
A promising frontier is the integration of IoT in agriculture, where smart sensors and devices help optimize crop management, monitor soil conditions, and enhance overall agricultural productivity.
IX. Exploring Ethical Considerations:
Ethical Use of Data:
As IoT devices collect vast amounts of data, there is a growing need to address ethical concerns regarding the use, ownership, and potential misuse of this data. It’s critical to strike a balance between responsible data handling and innovation.
Inclusive Deployment:
Ensuring that the benefits of IoT are accessible to all, irrespective of socio-economic factors, is essential. Ethical considerations include avoiding creating a digital divide and ensuring equitable access to the advantages offered by IoT.
Conclusion:
The Internet of Things is not just a technological evolution; it is a paradigm shift that is redefining how we interact with the world. As IoT continues to evolve, the smart web weaves become more intricate, connecting not only devices but shaping the way we live, work, and engage with our environment. From the mundane to the extraordinary, IoT is the silent architect of a future where connectivity is seamless, data is meaningful, and our world is truly smart. As we stand at the intersection of technology and connectivity, the potential of IoT to reshape our world is limited only by our imagination and our ability to address its challenges responsibly.